One of the many aspects that are integral to good money management in forex is position size. Position size in trading helps traders to minimize risks while maximizing rewards. The proposition of minimizing risk and maximizing rewards might sound like a silver bullet.
However, as you will discover in this article, calculating position size in forex trading is a bit of art, combined with a bit of logic. This article on position sizing in forex will enable you to understand how you can use this approach to let your winning trades make the most of the market.
Before we go into the details of position sizing in forex, let’s briefly talk about the issues facing this. After all, if position sizing is all about maximizing profits, you may wonder why trading statistics show that most traders lose money.
The answer to this is that depending on leverage and capital, different traders tend to enter the trade with different contract sizes or lots. Secondly, not everyone follows the trading rules and even if they do, the trading rules can differ from one trader to another.
Knowing how much to risk is key to the variability of the subjectivity of forex trading. This falls under the purview of forex risk management. Risk management is essential for trading. Many traders don’t pay much attention to this.
Position sizing is all about utilizing an effective method to determine the risk you take within your trading strategy. This is a better approach instead of risking all of your trading capital (a classic mistake that many beginners do).
It is important that a trader know beforehand how many lots they plan to trade and how that will impact their risk. Now, let’s get into the details of calculating position sizing in forex.
Explain what is position size in forex?
In general trading or investing terminology, position size is defined as the size of a position a trader takes. In other words, position size is the dollar amount that an investor is putting into a trade. Position sizing helps traders to understand how many units of an instrument they will be trading, based on its dollar value.
Hence, position size essentially tells you the risk you are taking for a trade. In general terms, from a forex trading terminology, position sizing is all about deriving your maximum profit or loss based on your take profit and stop loss levels.
This will give you the absolute dollar value of the risk and reward you take (depending on the contract size you use). Position sizing in forex also goes closely with the one percent risk rule. The one percent risk rule dictates that you should not risk more than one percent of your total available equity on trade.
By implementing position sizing, traders can then derive their maximum risk and compare it to the equity to find out how much they are risking on that trade. By extension, this could sometimes mean that traders will have to look for trade ideas that offer a minimum of 1:2 or a higher risk-to-reward ratio.
This forms another part of risk management. By some means, you can simply trade with a 1:1 risk-to-reward ratio as well. However, this would limit the longevity of your trading journey.
What is positions in position sizing?
The term position in position sizing refers to the trade and amount that is at stake. Positions, as you may know, can be either a long position or a short position. A long position is when the trader expects the price to rise and thus takes a long position (or is the buyer). A short position is when the trader expects the price to fall. This makes them take a short position or (being a seller in the market.)
How to calculate position size in forex?
There are a few things that traders need to keep in mind when calculating the position size in forex.
- Your trading equity, or the total amount available to trade in your forex trading account
- What is the amount that you are willing to risk per trade (in dollar value)
Once you are armed with the above information, you can then proceed to a trade level. Here, it starts with:
- Following a trading strategy and thus, the stop loss, entry and take profit levels
- Convert these levels (stop loss and take profit) into dollar values based on the contract size you want to trade
- This will now give you the absolute dollar values for your trades, in terms of risk and reward
In the process of figuring out the above three steps, you may also need to look into calculating the pip size for the currency pair that you are trading.
A basic example of position sizing in forex
Let’s break this down into a simple example.
Assume that you have $1000 in your trading account. You decide that you want to risk 10% of your equity. This would mean that you are willing to risk $100 per trade.
Now let’s assume that you found a good trading opportunity on the EURUSD currency pair giving you a risk-to-reward ratio of 1:2. In other words, your trade will give you $200 in profit for the $100 you are willing to risk on that trade.
From here on, the next step is in the contract size itself. For the EURUSD currency pair, a 1 lot equals 100,000 units. This means that a one-pip move in the EURUSD currency pair will equate to $10.
Hence, we can now break this down into the stop loss in pips.
| Contract Size | Pip Value | Pips (for stop loss) |
| 1 Lot (100,000) | $10 | 10 pips |
| 1 Mini Lot (10,000) | $1 | 100 pips |
| 1 Micro Lot (1000) | $0.10 | 1000 pips |
From the above, you can now deduce whether you want to go for a 1-lot trade or a 1-mini lot trade. This will obviously depend on how far out your stop loss will be. But the overall goal of this example is that position sizing at the very basic level will dictate how much of a trade size you want to enter with.
With a basic understanding of position sizing, let’s look at the different position sizing strategies or approaches that a trader has at their disposal.
Types of forex position sizing methods
There are different ways to deduce the position sizing which are briefly outlined below:
Fixed dollar value method
In this approach, the risk is essentially transformed into the absolute dollar values that you will be risking, based on the trading position size. An example of this was covered in the previous section. In this approach, you essentially determine how much in dollars you want to risk on a trade and based on that, you can pick the corresponding lot size for the trade.
While the example given is that of EURUSD, you can apply the same to just about any forex instrument that is a major (where USD can be the base or the quote currency).
The fixed dollar approach is the simplest of all and is recommended if you are just starting out. Of course, using an arbitrary number would not make sense. Therefore, it is best to use the fixed percentage method, which is more objective for your trading capital.
Fixed percentage method
The fixed percentage approach is essentially an enhancement of the fixed dollar method. The only difference here is that by picking an arbitrary dollar value, you would derive this number as a percentage of risk.
For example, if you want to risk 1% on the trade, then depending on your trading capital you find the dollar value which is one percent of your trading capital. The absolute dollar value here is now derived as a percentage of your capital.
From here on, you continue on as outlined in the example to determine how many lots you want to trade. The decision on how much percentage to the risk of course depends on your risk tolerance. The one percent risk is merely a generalization that is widely quoted among various forex articles.
At the end of the day, if you are comfortable to risk 2% or even 5%, then you can use this to derive the position size you want to trade.
There are other factors to consider for the above two methods as well, this includes your trading leverage as well, which is another aspect to keep in mind.
Using the Kelly Criterion for position sizing
The Kelly criterion is a statistical formula that will tell you how much you should risk. This is a purely objective way of deriving the number based on your past trading history. Simply put, Kelly criteria determine the optimal investment a trader can make based on probability.
The formula for using the Kelly criteria is as follows:
f* = (bp – q)/b
- f* is the fraction of the investment to make
- b is the net odds on the trade (the pay-out minus the probability of losing)
- p is the probability of winning
- q is the probability of losing or simple (1 – p)
Another common formula you may come across for the Kelly criterion (K%) is:
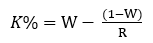
W = the winning probability
R = Win/loss ratio
The Kelly criterion of course has its own benefits and pitfalls. On the plus side, the Kelly criterion helps to maximize long-term growth and it also accounts for the risk and return of the investment. The good part is that the Kelly criterion can be applied to a wide range of trading instruments.
On the downside of the Kelly criterion approach, the model assumes that the probability of wins and losses is always known, which in reality isn't the case. Secondly, the Kelly criterion does not account for the risk tolerance of the investor. It simply spits out a number.
In the event that (which is most often the case) the investment performs badly, it can translate to large losses. By default Kelly criterion leads to higher volatility in your PnL.
And last but not the least, the Kelly criterion is pointless to use for small investors, which is most often the case with forex traders. The additional risk of course comes with leverage, which is widely prevalent in the retail forex world.
Forex position sizing – Conclusion
Position sizing in forex is vital to your overall risk management approach. But this is not the end-all and be-all to being a successful forex trader. The position sizing method is just one of the different aspects of trading.
You will of course need to consider your trading strategy, your approach to the markets and most importantly, the market conditions themselves. No matter what you use in your trading, you should be primarily aware of the fact that you can still lose money.
While the concepts of risk management may seem appealing, they in no way guarantee you success or being able to make money all the time. But having said that, forex position sizing and other aspects of trading will help you to become a better trader.
More importantly, this objective approach will help you to become a more disciplined trader, rather than one trading by emotions that are dictated by the markets and your recent string of wins and losing trades.
As a trader, perhaps the first step to all of this begins with knowing what you want to achieve with trading. Having an understanding of the number of profits you want to make (over the year) will become the starting point of your position sizing plan.
A trader who wants to make 10% or higher profits will of course need to tolerate higher risks as compared to a trader aiming for conservative growth over the year. At the end of the day, following risk management principles in the trading will, by no means guarantee you success. But what it will do is keep you on the right track, while maximizing your chances of putting on a trade.

